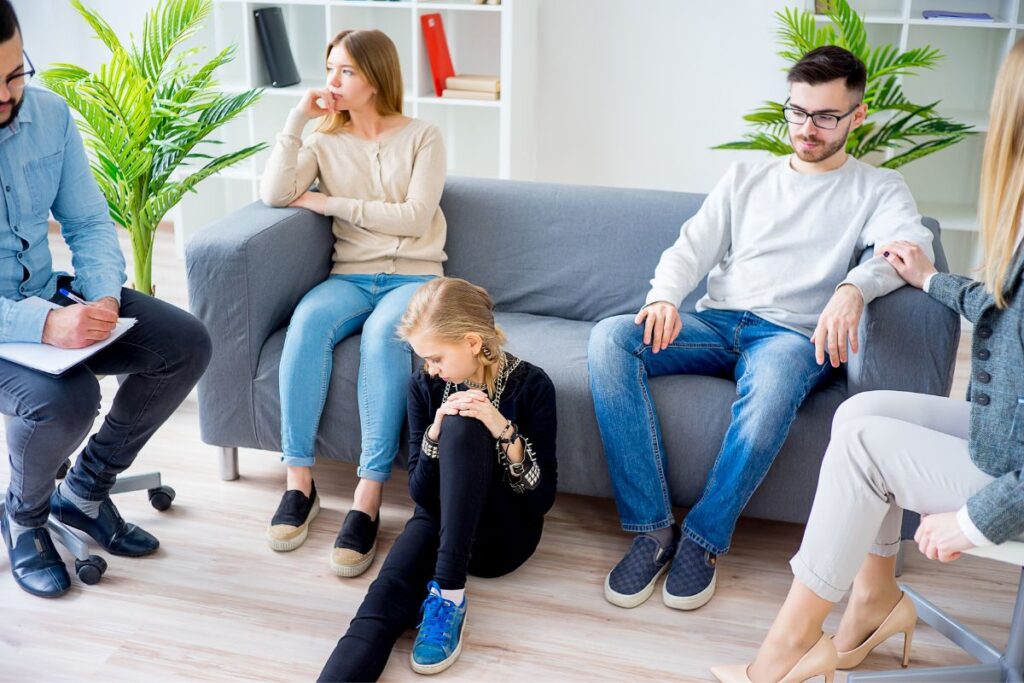
How Does Family Therapy Improve Communication & Connection?
Open communication and deep connections are the foundation of a healthy, thriving family. Yet, in the fast pace of modern life, these vital elements often take a backseat, leading to misunderstandings, unresolved conflicts, and emotional distance between loved ones. If your family is struggling with disconnection, you’re not alone—many families face similar challenges.
The good news? These issues can be addressed, and relationships can be restored with the right approach. Family therapy is a powerful solution that helps improve communication, resolve conflicts, and strengthen emotional bonds. With the guidance of a skilled therapist, your family can navigate challenges in a safe, supportive space, fostering understanding and deeper connections.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional medical or psychological advice. Family therapy outcomes vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult a licensed therapist or mental health professional for personalized guidance. If you or a family member are experiencing severe emotional distress, seek immediate support from a qualified professional or crisis service.

Navigating Family Dynamics: Understanding Roles and Communication
Family dynamics shape the way members interact, influencing everything from emotional connections to daily routines. These dynamics develop based on individual roles, communication styles, and past experiences. A healthy family dynamic fosters mutual respect and understanding, while an imbalanced one can lead to tension and unresolved conflicts.
Each family member plays a role that impacts the overall balance. Some naturally take on caretaker responsibilities, while others may feel overlooked or unheard, creating potential friction. The primary goal of improving family dynamics is to foster mutual understanding and healthy communication. Open, empathetic discussions build stronger connections, while poor or hostile communication can lead to resentment and emotional distance. Recognizing these patterns is the first step toward fostering a more supportive and harmonious family environment.
How Past Experiences Shape Family Dynamics and Communication
Significant life events and past traumas can deeply influence family relationships, often creating lasting emotional challenges. Unresolved feelings of anger, mistrust, or guilt can lead to strained communication, causing family members to develop unhealthy coping mechanisms such as avoidance, aggression, or emotional withdrawal. If left unaddressed, these patterns can make open and honest dialogue difficult, reinforcing negative cycles within the family unit.
For instance, a controlling family member may unintentionally silence others, leading to frustration and emotional distance. Similarly, families affected by past trauma might resort to avoidance, making it even harder to foster meaningful connections. Over time, these dynamics can erode trust and create an environment where open communication feels impossible.
However, family therapy offers a path toward healing. A professional therapist helps families recognize and address these unhealthy patterns, guiding them through open, empathetic discussions. By resolving past conflicts and improving present communication, therapy strengthens family bonds, creating a healthier and more supportive environment for the future.
How Communication Shapes a Healthy Family Dynamic
Strong communication is the foundation of a thriving family. It goes beyond just exchanging words—it’s about understanding emotions, intentions, and the deeper concerns that influence relationships. When family members feel heard and valued, they are more likely to express themselves openly, fostering trust and reducing misunderstandings. This creates a supportive environment where conflicts can be resolved more effectively.
On the other hand, poor communication can take a serious toll on family health. Misunderstandings, recurring arguments, and emotional distance can gradually erode relationships, leading to resentment and frustration. Over time, these unresolved issues can intensify, creating a cycle of negativity that may feel impossible to break without intentional effort or professional guidance. Prioritizing open and honest communication is essential for maintaining strong, healthy family connections.
How Family Therapy Strengthens Relationships and Resolves Conflicts
Family therapy plays a crucial role in breaking down communication barriers and fostering healthier relationships. A skilled therapist identifies underlying issues and provides practical strategies to enhance understanding and connection among family members.
Through active listening, unbiased guidance, and proven communication techniques, therapy helps families navigate conflicts and build stronger bonds. When communication improves, each member feels heard, valued, and supported, leading to a more harmonious and resilient family dynamic. Investing in better communication today creates lasting emotional well-being for everyone.
Effective Communication Strategies for Stronger Family Bonds
Improving family communication is key to building deeper connections and resolving conflicts in a healthy way. In family therapy, professionals use proven techniques to encourage open, respectful, and productive conversations. These strategies aren’t just for therapy sessions—they can be easily applied in everyday life to create a more supportive home environment. Here are some practical techniques to enhance communication within your family:
Active Listening: Fostering Understanding and Respect
Active listening is a powerful technique that strengthens family relationships by ensuring every member feels heard and valued. This involves giving full attention to the speaker, avoiding interruptions, and responding with thoughtful input. When family members actively listen, they demonstrate respect and empathy, creating a safe space for open communication. For example, if a loved one is expressing their emotions, responding with validation—rather than dismissing their feelings—helps build trust and deeper connections.
Assertiveness Training: Expressing Needs with Confidence
Assertiveness training teaches individuals how to communicate their thoughts, feelings, and needs clearly and respectfully. This technique empowers family members to set boundaries and express themselves without resorting to aggression or passive avoidance. By learning to assert their needs while also respecting others, family members can prevent misunderstandings and reduce conflicts. For example, instead of bottling up frustrations, one might say, “I need some quiet time in the evening to relax; can we agree on a noise level that works for everyone?”
Nonviolent Communication: Building Empathy and Connection
Nonviolent communication (NVC) encourages speaking in a way that fosters empathy and understanding, rather than blame or hostility. This method involves expressing feelings and needs while being mindful of others’ emotions. Families practicing NVC can resolve conflicts more peacefully, strengthening their emotional bonds. A simple example is replacing accusatory language with constructive statements, such as, “I feel hurt when I’m interrupted, and I’d appreciate it if we could take turns speaking.” By adopting this approach, families can nurture healthier, more harmonious relationships.
Applying These Techniques to Strengthen Family Communication
Integrating these communication techniques into family life can take practice, but the results are well worth the effort. A therapist can offer practical strategies to help families implement these methods in everyday interactions. For example, scheduling regular family meetings can create a structured space to discuss concerns, resolve conflicts, and reinforce active listening skills.
Another effective approach is role-playing exercises, which allow family members to practice expressing their thoughts assertively while respecting each other’s boundaries. With professional guidance and consistent effort, families can transform their communication patterns, leading to stronger relationships and a more supportive home environment.
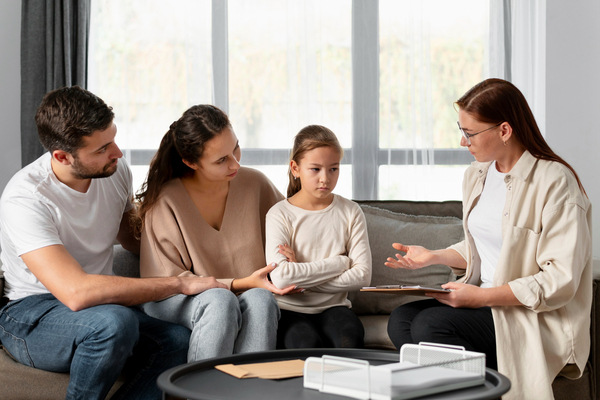

Strengthening Family Connections Through Therapy
Good communication is important, but strong emotional bonds are the foundation of a healthy family. Family therapy goes beyond surface-level interactions, helping loved ones build deeper connections by identifying and resolving underlying issues that may be creating distance. Through guided sessions, families can foster emotional intimacy, rebuild trust, and create a more supportive home environment.
Strengthening Family Bonds Through Engaging Activities
A therapist may incorporate structured activities and exercises to help families build stronger emotional connections. These can range from trust-building exercises and role-playing scenarios to simple yet meaningful activities like cooking a meal together. Engaging in these activities fosters open communication, encourages teamwork, and deepens emotional bonds. For example, cooking as a family not only improves collaboration and problem-solving skills but also creates a shared experience that strengthens relationships. By participating in these exercises, family members develop a greater sense of trust and understanding, ultimately improving their overall connection.
Strengthening Family Bonds Through Life Transitions with Therapy
Major life changes—such as divorce, remarriage, losing a loved one, or relocating—can disrupt family dynamics, leading to stress and conflict. Family therapy offers essential support, providing guidance to help families adapt, communicate effectively, and navigate emotional challenges. With the right therapeutic approach, families can build resilience, strengthen relationships, and create a healthier path forward.
For instance, during a divorce, therapy helps family members process complex emotions and adjust to new family structures while prioritizing children’s emotional well-being. When coping with loss, therapy provides a space to grieve, heal, and honor a loved one’s memory in a meaningful way. For families moving to a new location, therapy can ease the transition by addressing stress, uncertainty, and the emotional impact of change. No matter the challenge, family therapy equips families with the tools to move forward together with understanding and support.
Maintaining Progress After Therapy: Strengthening Family Bonds
Therapy doesn’t end when the sessions do—it’s what you do afterward that truly solidifies lasting change. The key to sustaining progress is consistently applying the communication and coping strategies you’ve learned. By integrating these techniques into daily life, you can continue to strengthen relationships and navigate future challenges with confidence.
One of the most impactful ways to maintain growth is through effective family communication. Regular check-ins, using “I” statements during conflicts, and practicing active listening can help foster a supportive and connected home environment. These small but intentional efforts ensure that the progress made in therapy extends into everyday interactions, reinforcing emotional bonds over time.
Even after therapy ends, the work doesn’t stop. Families who commit to open and respectful communication can continue to deepen their connections and handle life’s transitions with resilience. By making these strategies a consistent part of family life, you create a foundation of understanding, trust, and long-term emotional well-being.
Conclusion
Family therapy is a powerful tool for improving communication, resolving conflicts, and strengthening emotional connections. By understanding family dynamics, addressing past experiences, and adopting effective communication strategies, families can create a more supportive and harmonious home environment. Techniques like active listening, assertiveness training, and nonviolent communication help foster deeper relationships, while structured activities and therapy sessions provide practical ways to build trust. For families navigating co-parenting, therapy offers essential guidance on maintaining consistency, setting healthy boundaries, and ensuring children feel secure and supported. Even after therapy ends, maintaining progress requires ongoing effort and intentional communication. With the right approach, families can navigate life’s challenges with resilience, ensuring lasting emotional well-being. Investing in better communication today creates a foundation of trust, understanding, and connection that will benefit every family member for years to come.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional medical or psychological advice. Family therapy outcomes vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult a licensed therapist or mental health professional for personalized guidance. If you or a family member are experiencing severe emotional distress, seek immediate support from a qualified professional or crisis service.
FAQs
1. How does family therapy improve communication?
Family therapy creates a safe space for open discussions, helping family members express their thoughts and emotions clearly. Therapists teach active listening, role-playing, and conflict-resolution strategies to strengthen communication and build understanding.
2. What key benefits does family therapy provide for strengthening relationships?
Family therapy improves communication, resolves conflicts, and strengthens emotional bonds. It helps family members recognize unhealthy interaction patterns and replace them with positive, supportive behaviors.
3. Can family therapy solve long-term communication problems?
Yes, family therapy identifies the root causes of poor communication and provides practical tools to create lasting change. When families consistently apply these strategies, they develop healthier, more effective ways to connect and interact.
4. How do therapists encourage open and honest conversations?
Therapists guide families through structured communication exercises that promote trust and understanding. They teach techniques like using “I” statements, practicing nonviolent communication, and de-escalating conflicts to create more meaningful conversations.
5. Does family therapy work for all types of family conflicts?
Family therapy helps resolve a variety of issues, including miscommunication, parenting struggles, sibling rivalry, divorce-related stress, and grief. Therapists customize sessions to address each family’s unique challenges, making therapy a valuable tool for improving relationships.
Users Also Say:
What do others think about how family therapy improves communication and connection?
Pml****
You can lead by example and create natural opportunities to encourage your family. If you’re not already in therapy, consider starting yourself. Share your experience with them—talk about what you’re learning, how it’s helping you, and the ways it’s improving your relationships. When they see the positive impact, they may become more open to the idea.
If your family shows interest, introduce therapy as a way to build on their strengths rather than fix problems. Instead of saying, “You all seriously need therapy”, which might trigger defensiveness, focus on the benefits. Highlight how therapy has helped you and frame it as a tool that could enhance your family’s existing strengths. When they start asking questions, that’s your opportunity to suggest it in a supportive and constructive way.
Jumpin*******
Family therapy helps parents, children, and siblings improve communication and understand one another. A family therapist helps families recognize how their interactions influence behavior. Rather than focusing on individuals, family therapy examines the entire system—the complex dynamics that contribute to dysfunction.
A family counselor offers many benefits, especially in times of crisis. Seeking help as soon as possible can make a significant difference. Below are nine common benefits of family counseling:
- Improving Communication Within the Family
- Strengthening Relationships and Bonds
- Boosting Self-Esteem
- Creating a Happier Family Environment
- Building Stronger Family Connections
- Supporting Mental and Physical Well-Being
- Strengthening Marriage and Family Foundations
- Developing Coping Skills for Life Transitions
- Enhancing Parent-Child Communication
Utkarsh******
A family functions much like the human body—each part influences the others. Every family experiences both joyful moments and challenges. When conflicts, mental health struggles, or major life adjustments arise, family therapy can provide the support needed to navigate them. It fosters mutual understanding, encourages open emotional expression, and strengthens relationships. With the right guidance, families can break unhealthy patterns, resolve lingering tensions, and create a more supportive home environment. Seeking help from an experienced family therapist or psychologist can equip your family with the tools needed to build healthier communication and deeper connections.